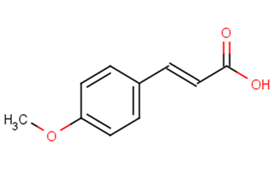
4-Methoxycinnamic acid
CAS No. 830-09-1
4-Methoxycinnamic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M20610 CAS No. 830-09-1
4-Methoxycinnamic acid is an unusual phenylpropanoid involved in phenylphenalenone biosynthesis in Anigozanthos preissi.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 45 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Methoxycinnamic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Methoxycinnamic acid is an unusual phenylpropanoid involved in phenylphenalenone biosynthesis in Anigozanthos preissi.
-
Description4-Methoxycinnamic acid is an unusual phenylpropanoid involved in phenylphenalenone biosynthesis in Anigozanthos preissi.
-
In Vitro4-Methoxycinnamic acid is an unusual phenylpropanoid involved in phenylphenalenone biosynthesis in Anigozanthos preissii.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number830-09-1
-
Formula Weight178.18
-
Molecular FormulaC10H10O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (280.62 mM)
-
SMILESCOc1ccc(\C=C\C(O)=O)cc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Funk C Brodelius P E . Phenylpropanoid Metabolism in Suspension Cultures of Vanilla planifolia Andr. : III. Conversion of 4-Methoxycinnamic Acids into 4-Hydroxybenzoic Acids[J]. PLANT PHYSIOLOGY 1990 94(1):102-108.
molnova catalog



related products
-
5-Methoxytryptophol
5-Methoxytryptophol is a pineal indoleamine derived from serotonin shown to be biologically active in a number of species.
-
DL-3-AMINOISOBUTYRIC...
beta-aminoisobutyric acid is the product from the conversion of N-carbamyl-beta-aminoisobutyric acid by the enzyme Beta-ureidopropionase (EC 3.5.1.6) the last step in pyrimidine degradation. Beta-ureidopropionase deficiency is an inborn error of pyrimidine degradation associated with neurological abnormalities.
-
26-Dihydroxybenzoic ...
26-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a secondary metabolite of salicylic acid which has been hydrolyzed by liver enzymes during phase I metabolism.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


